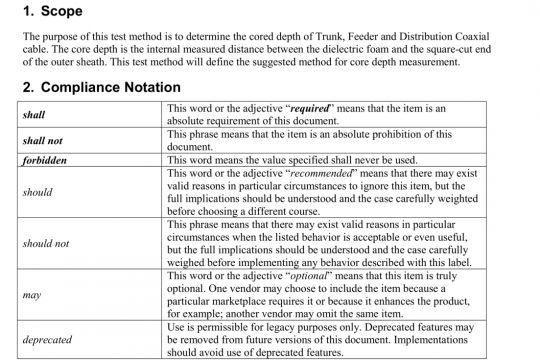
ANSI X9.129 pdf free download
ANSI X9.129 pdf free download.Legal Orders Exchange.
4.2.2 Requester Supplemental Information Record (Type 10)
The Requester Supplemental Information Record (Type 10) shall be present and always follow the File Header Record (Type 01). It is a mandatory record with one record per file.
4.2.3 Request Content Record (Type 20)
The Request Content Record (Type 20) shall be present and always follow the Request Supplemental
Information Record (Type 10). There shall be one content record for each case in the file.
4.2.2 Request Debtor Record (Type 25)
The Request Debtor Record (Type 25) is a mandatory record to identify each customer in a legal order case and will always follow the Request Content Record (Type 20). There shall be one debtor record per customer.
4.2.3 Request Account Record (Type 26)
The Request Account Record (Type 26) is a conditional record available to provide an order to a specific account only and will always follow a Request Debtor Record (Type 25). There shall be one account record per account.
4.2.4 Maintenance Request Record (Type 40)
The Maintenance Request Record (Type 40) shall follow the Request Debtor Record (Type 25) or the conditional Request Account Record (Type 26). This record type is conditional and used by the Requester to provide the action for the Financial Institution to take on an existing case.
4.2.5 Response Supplemental Information Record (Type 11)
The Response Supplemental Information Record (Type 11) shall be present and always follow the File Header Record (Type 01). It is a mandatory record with one record per file.
4.2.6 Response Content Record (Type 30)
The Response Content Record (Type 30) shall be present and always follow the Response Supplemental Information Record (Type 11). There shall be one content record for each case in the file. All records within the Response Content Record (Type 30) must have a match to and be in the same order as in the Request Content Record (Type 20).
4.2.7 Follow Up Response Content Record (Type 31)
The Follow Up Response Content Record (Type 31) is identical to the Response Content Record (Type 30). It is a conditional record used to provide the full response to a specific point in time or continuous case with action pending.
4.2.8 Response Debtor Record (Type 35)
The Response Debtor Record (Type 35) is a mandatory record to identify each customer in a legal order case and will always follow the Response Content Record (Type 30). There shall be one response debtor record per customer.
4.2.9 Response Account Record (Type 36)
The Response Account Record (Type 36) is a conditional record to provide a response to the account(s) in the Request Account Record (Type 26). There shall be one response account record for each account and will always follow the Response Debtor Record (Type 35).
4.2.10 Amended Response Content Record (Type 51)
The Amended Response Content Record (Type 51) will follow the Response Content Record (Type 30) or the Follow Up Response Content Record (Type 31). This record type is conditional and used by the Financial Institution to provide an updated response to a specific case.
4.2.11 User Defined Record (Type 60-79)
The User Defined Record (Type 60-79) is a conditional record reserved for future use to provide data exchange flexibility between the Requester and Financial Institution.
4.2.12 File Control Record (Type 99)
The File Control Record (Type 99) shall be present as the last record in a request file and the last record in the response file.
5 Data and Field Specifications
5.1 Generic Data Types
The following are the names, abbreviations, and definitions of the characters permitted in the standard.
Unless otherwise stated in applicable agreements, all characters and symbols will be represented using 8bit ASCII rules between the sender and receiver. Non ASCII characters are not permitted.
5.1.1 Alphabetic (A)
The alphabetic characters are the upper case letters A through Z; the lower case letters a through z, and the blank (space) character. When lower case letters are used, they shall be interpreted to have the same meaning as their respective upper case letters, e.g., no distinction shall be made between the upper case letter A and the lower case letter a.
ANSI X9.129 pdf download.