CSA ANSI Z21.93 pdf free download
CSA ANSI Z21.93 pdf free download.Excess flow valves for natural gas and propane gas with pressures up to 5 psig.
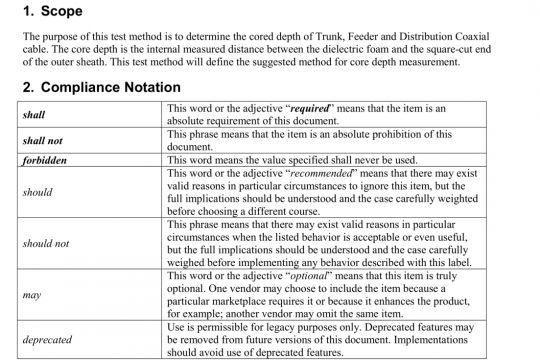
3 Definitions
The following definitions shall apply in this Standard:
Body — The principal structure of a device that contains and supports an actuating mechanism and constitutes the main gas passage.
BTU — Abbreviation for British Thermal Unit. The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 pound of water 1°F.
Excess flow valve, (EFV) — A device installed in a fuel gas piping system to automatically trip when the rate of passage of fuel gas through the device exceeds a predetermined level (trip flow).
Excess flow valve bypass, (EFVB) — An excess flow valve designed to limit the flow of fuel gas after trip of the excess flow valve to a predetermined level and to reset automatically after the pressure is equalized across the valve.
Excess flow valve non-bypass, (EFVNB) — An excess flow valve designed to stop the flow of fuel gas after trip of the excess flow valve and to be reset manually.
Bypass flow — An internal rate of passage of fuel gas through an bypass excess flow valve after trip of the bypass excess flow valve, which will allow upstream and downstream pressure to equalize across the device to automatically reset to the open position.
Liquefied petroleum gases — The terms “Liquefied Petroleum Gases,”“LPG” and “LP-Gas” as used in this standard means and includes any material that is composed predominantly of any of the following hydrocarbons, or mixtures of them; propane, propylene, butanes (normal butanes or isobutane), and butylenes.
Maximum flow capacity — The highest rate of passage of fuel gas through an excess flow valve specified by the manufacturer that allows for normal operation of the appliance(s) the excess flow valve serves. This shall not be more than 90 percent of rated trip flow.
Orifice — The opening in a cap, spud, or other device whereby the flow of gas is limited and through which the gas is discharged to the burner.
Rated trip flow — The minimum trip value as specified by the manufacturer that will cause the excess flow valve to stop of limit the flow of fuel gas.
Reset — Changing the position of an excess flow valve from a closed to an open position.
4 Construction
41 General
4.1.1
The construction of parts not covered by this Standard shall be in accordance with reasonable concepts of safety, substantiality and durability. All specifications as to construction set forth herein may be satisfied by the construction actually prescribed or such other construction as will provide at least equivalent performance.
4.1.2
Materials, assembly, workmanship and design should be of a good quality with parts well fitted.
4.1.3
The mechanisms of valves shall be protected by substantial housing so as to prevent interference with the safe operation of the devices.
4.1.4
Pins, stems or other linkages passing through the valve body or housing shall be sealed to provide gas tight construction.
4.1.5
Valves shall be constructed to discourage disassembly in the field. Construction that requires the use of a special tool for disassembly is considered to meet this provision.
4.1.6
Moving parts shall be protected against abrasion and shall be guided or arranged to minimize binding, buckling or other interference with their free movement.
4.2 Equipment and data to be furnished by the manufacturer
The manufacturer shall furnish the following equipment and data to the testing agency:
a) Representative valves, as specified by the testing agency;
b) Drawings, blueprints, photographs which describe each model valve as specified by the testing agency;
c) Minimum and maximum operating pressure (in appropriate units, inches of water, pounds per square inch, and metric equivalents);CSA ANSI Z21.93 pdf download.